Virus structure
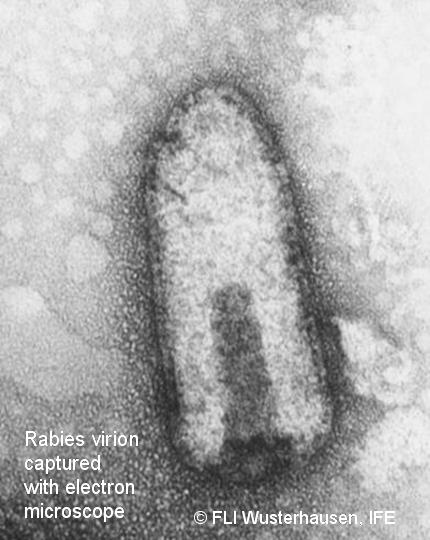 The RNA genome of
Lyssaviruses is 12 kilobases long, non-segmented and of negative
polarity encoding five viral proteins (3´ to 5´): nucleoprotein N,
phosphoprotein P, matrix protein M, glycoprotein G and polymerase L. The
bullet-shaped lyssavirus particle has 100–300 nm in length and 75 nm in
diameter. It is composed of two structural and functional units:
The RNA genome of
Lyssaviruses is 12 kilobases long, non-segmented and of negative
polarity encoding five viral proteins (3´ to 5´): nucleoprotein N,
phosphoprotein P, matrix protein M, glycoprotein G and polymerase L. The
bullet-shaped lyssavirus particle has 100–300 nm in length and 75 nm in
diameter. It is composed of two structural and functional units:
The lipid bilayer from the host cell builds the outer
envelope. It is covered with spike like projections corresponding to
G-Protein trimers, which recognise and bind cell receptors. The
G-Protein is essential for lyssavirus pathogenicity and for the
induction of the immune response.
The internal ribonucleokapsid (RNP) is of helical
structure and is composed of the genomic RNA intimately associated with
protein N, polymerase L and its cofactor protein P (formerly named M1).
The ribonucleocapsid complex ensures genome transcription and
replication in the cytoplasm.
The matrix protein M (formerly named M2) occupies an
intermediate position between the ribonucleocapsid and the envelope, and
is responsible for virus budding and the bullet-shaped morphology.